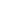
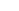
2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, commonly known as HEMA, stands as a cornerstone in various industrial and medical applications. This versatile monomer has revolutionized multiple sectors due to its unique chemical properties and exceptional adaptability. Its ability to form copolymers and its excellent biocompatibility have made it an invaluable component in numerous products we encounter daily.
The significance of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate lies in its molecular structure, which combines hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. This dual nature enables it to interface effectively with both water-loving and water-repelling substances, opening up a wide range of applications across different industries.
In the realm of contact lens production, 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate plays a pivotal role. Its hydrophilic properties allow for the creation of soft contact lenses that maintain high water content, ensuring comfort and oxygen permeability. Modern contact lens manufacturers utilize HEMA-based materials to develop lenses that can be worn for extended periods while maintaining eye health.
The incorporation of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate in contact lens materials has led to significant improvements in lens durability and comfort. These advances have resulted in products that resist protein deposits and maintain their shape even after prolonged wear.
The dental industry heavily relies on 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate for various applications, particularly in dental adhesives and composites. Its ability to bond effectively with tooth structure while maintaining biocompatibility makes it an essential component in modern dental materials. Dental professionals utilize HEMA-based products for everything from cavity fillings to dental sealants.
The adhesive properties of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate enable strong bonds between dental materials and tooth surfaces, contributing to the longevity of dental restorations. This characteristic has revolutionized restorative dentistry, allowing for more durable and aesthetically pleasing results.
The coating industry has embraced 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate for its exceptional film-forming properties. When incorporated into coating formulations, it enhances adhesion, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. These characteristics make HEMA-based coatings ideal for various surfaces, from metals to plastics.
Industrial applications benefit from the chemical resistance and weatherability of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate coatings. These properties ensure long-lasting protection for treated surfaces while maintaining their aesthetic appeal under challenging conditions.

In adhesive production, 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate serves as a crucial component for developing high-performance bonding solutions. Its ability to create strong chemical bonds while maintaining flexibility makes it particularly valuable in this sector. Manufacturers utilize HEMA in various adhesive formulations, from construction adhesives to specialty bonding agents.
The versatility of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate in adhesive applications extends to both structural and non-structural bonding scenarios. Its compatibility with various substrates makes it an ideal choice for developing multi-purpose adhesive systems.
The field of tissue engineering has found numerous applications for 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate in developing scaffolds and biomaterials. Its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels make it particularly suitable for tissue regeneration applications. Researchers continue to explore new ways to utilize HEMA in creating advanced biomaterials.
The development of HEMA-based scaffolds has opened new possibilities in regenerative medicine, offering solutions for tissue repair and organ regeneration. These materials provide an ideal environment for cell growth while maintaining structural integrity.
2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate plays a crucial role in modern drug delivery systems. Its ability to form controlled-release matrices makes it valuable in pharmaceutical applications. These systems allow for precise drug release rates and improved therapeutic outcomes.
The development of HEMA-based drug delivery platforms has revolutionized how medications are administered, offering better control over drug release profiles and enhanced patient compliance. These innovations continue to drive advancements in pharmaceutical technology.
2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate's biocompatibility, ability to form hydrogels, and excellent mechanical properties make it ideal for medical applications. Its low toxicity and ability to maintain stable properties in biological environments contribute to its widespread use in medical devices and materials.
2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate improves coating performance through enhanced adhesion, durability, and chemical resistance. Its unique molecular structure allows for better surface wetting and strong bond formation with various substrates, resulting in more effective and longer-lasting coatings.
Yes, 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate can be incorporated into biodegradable materials when properly copolymerized with other biodegradable monomers. This capability has led to its use in developing environmentally friendly materials for various applications, particularly in the biomedical field.
 Hot News
Hot News2026-01-17
2026-01-13
2025-07-25
2025-06-16
2025-04-07
2025-04-07