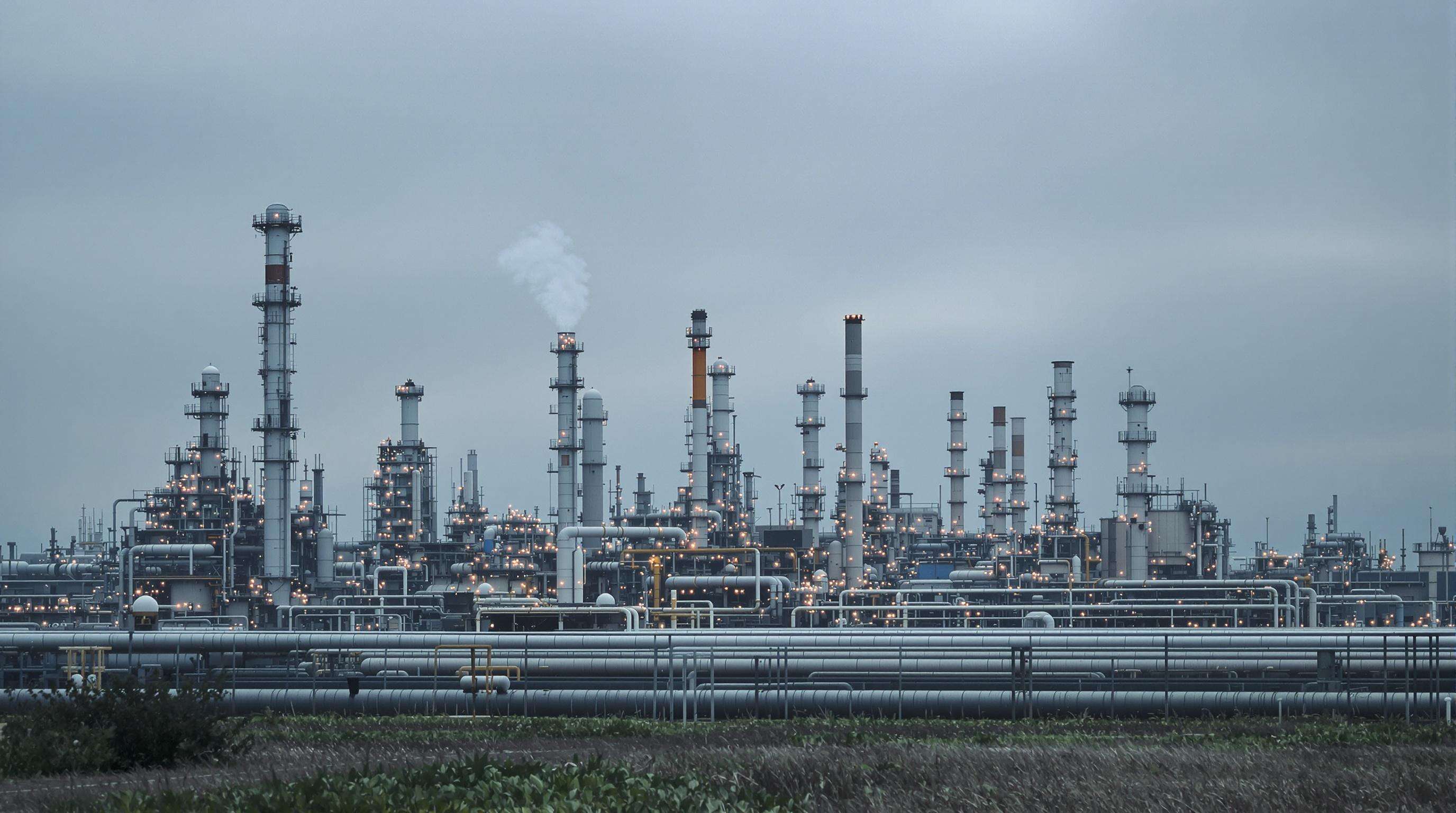
Traditional BA manufacturing emits 12–15 metric tons of CO₂ equivalents per ton of product, primarily due to energy-intensive petrochemical processes and VOC emissions (Ponemon 2023). Fossil fuel-dependent stages account for 74% of total emissions, with acrylic acid synthesis alone contributing 40% of process-related GHGs.
A recent Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) study reveals that 68% of BA’s carbon footprint originates from raw material extraction and refining. Transportation to emulsion producers adds 12% of emissions, while polymerization accounts for 20%. This granular data enables manufacturers to target decarbonization at the most impactful stages of the supply chain.
Emerging production methods reduce emissions by 38% through renewable energy integration in steam cracking, catalytic distillation that lowers reaction temperatures, and carbon capture retrofitted to acrylic acid plants. Third-party verified low-carbon BA grades now meet ISO 14067 standards for cradle-to-gate emissions, offering formulators a credible path to reducing environmental impact.
While 62% of suppliers claim "sustainable BA," only 34% provide verifiable evidence across plant-level emission audits, renewable feedstock traceability, and Scope 3 disclosures. The Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) warns that unverified carbon-neutral claims risk misleading environmentally-conscious emulsion formulators, emphasizing the need for transparent, audited sustainability reporting.
Butyl Acrylate, or BA for short, plays a key role in waterborne emulsion systems that cut down on VOC emissions by around 30 to 50 percent when compared to traditional solvent based products. Recent improvements in how these emulsions are made take advantage of BA's flexible molecular structure to produce strong binding agents used in things like wood stains and outdoor coatings while keeping VOC levels extremely low, typically below 50 grams per liter. Industry tests from last year showed that coatings made with modified BA acrylics resist alkaline conditions about 98 times out of 100 and stick better to surfaces by roughly 40%, meaning these protective coatings last much longer before needing replacement, which cuts down on wasted materials over time.
Companies working on BA materials have been tweaking those ester functional groups lately to get better biodegradability while still keeping the polymer properties intact. Mix these BA compounds with some bio-based co-monomers and they break down microbes in landfills about 28 percent quicker according to recent tests published in Nature last year. Pretty impressive stuff actually. The European Chemical Agency wants plastics to degrade at least 60% within just two years, so this kind of development helps manufacturers meet those requirements. While not quite there yet, BA seems like a good stepping stone on the path to completely plant-based acrylic solutions for the industry.
The field of BA applications is undergoing major changes thanks to three main advancements. First, there's the development of low temperature curing systems which can reduce energy consumption by around 35%. Second, we're seeing hybrid materials that actually contain about 15 to 20 percent recycled acrylic components. And third, self cross linking emulsions have emerged as a game changer because they completely remove formaldehyde emissions from the process. All these improvements are helping manufacturers comply with EPA regulations while also satisfying those tricky ESG investment requirements. According to recent market research from 2024, roughly seven out of ten coating companies are actively seeking out suppliers who specialize in low carbon BA solutions. This trend shows how critical sustainability has become across the industry landscape.
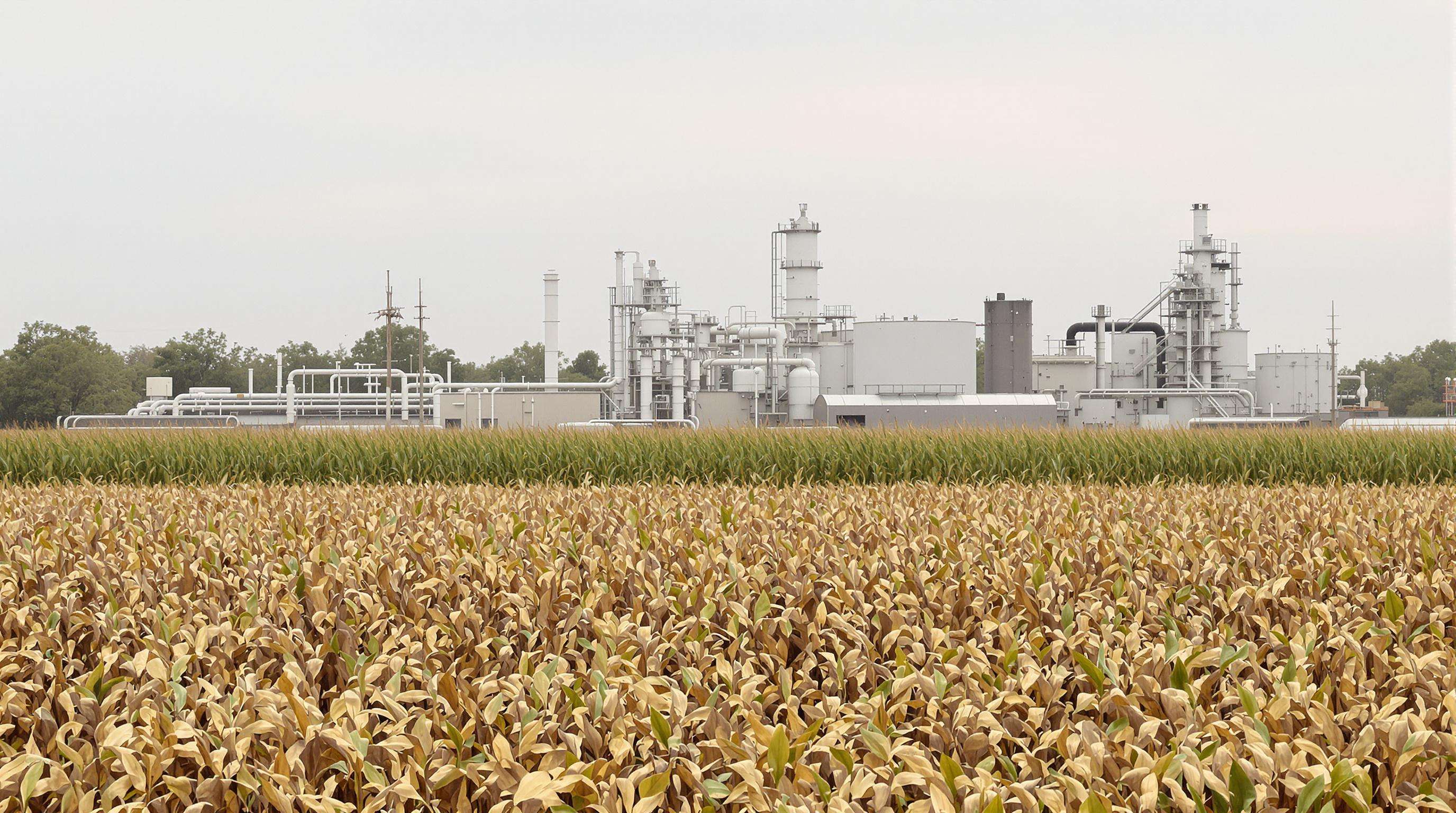

Chemical companies are moving away from traditional fossil fuels and starting to use things like corn, sugarcane, and cassava instead when making butyl acrylate products. According to research published in 2023 by Myriant Corporation along with OPX Biotechnologies, switching to these plant based materials reduces emissions during manufacturing by around forty percent compared to what happens with oil based processes. The market for these kinds of biobased polymers seems set to expand quite rapidly too. We're talking about growth rates somewhere near twelve percent each year until 2032 according to projections. This trend makes sense given how strict environmental regulations have become lately plus all those corporate commitments to being greener. Plus it fits right into circular economy thinking since waste from farming operations gets turned into useful acrylate compounds rather than going unused.
Bio based BA is now matching what traditional versions can do technically and actually making it into full scale production facilities. Prices for bio based BA hit around $2,300 per tonne in 2024 which sits about 15 to 20 percent above what we pay for the petroleum derived stuff, though this gap seems to be getting smaller as more gets produced. Major players in the industry are putting roughly a third to almost half of their research money towards improving both fermentation methods and those catalytic reactions that make everything work better. Looking ahead, most analysts expect worldwide demand for these bio based acrylates to grow three times over by 2027. The automotive and construction industries are leading this charge since they need materials that leave a smaller carbon footprint without sacrificing quality.
Bio-based butyric acid still has a long way to go when it comes to scaling up production. The truth is, making this stuff costs about 80% more than traditional methods using petroleum, mainly because of all the different types of raw materials available and how complicated the cleaning process gets. We just don't have enough systems in place across farms to collect all that waste material needed for production, which really slows things down in the supply chain. Plus, rules vary so much from one region to another that companies hesitate before investing serious money. On the bright side though, some interesting collaborations are starting to form between chemical manufacturers and agricultural businesses. Early tests at small scale refineries show promise too, cutting costs by around 22% when they combine different processing steps together. Not bad, but there's definitely room for improvement.
These days, global emission standards are pushing for over 60% cuts in VOCs from architectural coatings, which has made butyl acrylate the go-to ingredient for around 8 out of 10 formulations that meet these requirements. Looking at what the U.S. EPA released in 2024, they point out how well BA works even when VOC levels drop below 100 grams per liter. Paint manufacturers have taken notice too, with demand for those low odor products jumping nearly triple since the start of 2020. All this regulatory pressure is driving growth in the market for low VOC acrylics. Industry analysts expect this segment could hit almost $20 billion worldwide by the time we reach 2032, though actual numbers will depend on how quickly companies adapt their production methods.
Advanced esterification techniques enable BA formulations with 30–40% bio-based content, cutting cradle-to-gate emissions by 58% without compromising adhesive strength or weatherability. Independent testing confirms these hybrid systems meet LEED v5 criteria and achieve <1% VOC content in premium wood coatings—key advantages for manufacturers targeting green building certifications.
BA constitutes 68% of waterborne acrylic binders globally, valued for its surfactant compatibility and hydrophobicity. Modern BA-enhanced emulsions deliver over 10,000 hours of weatherability in 100% water-based systems, outperforming solvent-borne alternatives by 27% in UV resistance. Asia-Pacific leads adoption, with BA specified in 91% of eco-certified construction projects since 2023.
A big push toward ESG practices in the chemical industry is changing how BA gets produced. According to recent data from the Chemical Sustainability Initiative (2023), around two thirds of manufacturers have cut down on Scope 3 emissions by switching to renewable feedstocks. Meanwhile, closed loop systems are cutting energy consumption somewhere between 18 and 22 percent when compared to traditional batch methods, all while keeping that critical polymer grade purity intact. By ticking boxes for both UN Sustainable Development Goal 12 about responsible consumption and Goal 13 focusing on climate action, BA continues to play a vital part in creating circular economies across adhesive and coating applications throughout various industries.
Strict VOC rules from places like the EPA's TSCA Chapter 6 changes have really pushed growth in low emission BA formulas over the past few years, clocking in at around 34% compound annual growth rate since 2020. These days, water based acrylic coatings with BA components actually make up about 62% of what's being sold in industrial coatings markets, beating out traditional solvent based options when it comes to how long they last and how fast they cure. We're also seeing something interesting happen with these new bio acrylate blends that contain under half a percent petroleum stuff. Some analysts estimate this segment could be worth nearly three billion dollars in the green polymer tech space by the time we hit 2027, though nobody knows for sure exactly how things will play out.
Traditional BA manufacturing emits a significant amount of CO₂ equivalents per ton of product primarily because of energy-intensive petrochemical processes and VOC emissions.
The lifecycle assessment indicates that raw material extraction and refining contribute to the majority of BA's carbon footprint, followed by transportation and polymerization processes.
Using renewable feedstocks like corn and sugarcane reduces emissions during manufacturing and aligns with circular economy practices, promoting more sustainable BA production.
Yes, bio-based BA production faces cost challenges and regulatory discrepancies across regions, but ongoing collaborations between chemical manufacturers and agricultural businesses are promising.
ESG principles are driving changes in BA production, with a significant push towards reducing emissions and adapting sustainable practices in alignment with global environmental goals.
 Hot News
Hot News2026-01-17
2026-01-13
2025-07-25
2025-06-16
2025-04-07
2025-04-07